Oi-Shan Tang
Speeches:
-
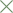
Different routes of administration
Oi-Shan Tang, MD
Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology,
The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong
Misoprostol is widely used in obstetrics and gynaecology. It is a prostaglandin E1
analogue licensed for oral use. However, vaginal administration has become a common
practice. However, women prefer to take the drug by mouth as this can avoid the
uncomfortable vaginal examination and provide more privacy during medical abortion.
Therefore, other ways of administration like sublingual route have been explored.
A pharmacokinetics study has compared the absorption kinetics of these three commonly
used routes of administration of misoprostol. It was shown that both the sublingual and
oral administrations have the quickest onset of action. Sublingual administration achieves
the highest plasma concentration. The systemic bioavailability as measured by the area
under the curve (AUC) is also highest among the three routes. The AUC360 after oral
administration was only 54 % of that after sublingual administration.
Many clinical studies have shown that vaginal misoprostol performed better than similar
doses of oral misoprostol in medical abortion. This is probably due to the more sustained
serum concentration after vaginal administration. The new sublingual route has been
shown to have a similar complete abortion rate to vaginal misoprostol in first trimester
medical abortion. However, it might be associated with higher incidences of side effects.
This may be related to its higher peak concentration. On the other hand, a short time to
Tmax and a higher Cmax make the sublingual misoprostol a good cervical priming agent. Its
clinical efficacy as a cervical priming agent has been proven. Sublingual misoprostol has
also been used for the management of postpartum haemorrhage. Its unique way of
administration makes it the route of choice in the presence of vaginal bleeding and when
oral intake is not desirable.
In conclusion, pharmacokinetics studies have demonstrated the absorption kinetics of
various routes of administration of misoprostol. More studies are required to find out the
best way of administration of misoprostol for various clinical applications.
